MetaWear Guide Series Part 6
Logging Data
This is part 6 of a multipart series showing you how to get started with the MetaWear platform. View the contents of the series to easily skip forwards or backwards
In the previous section we saw how to stream data. Streaming is, for most applications, the way to go. However, it requires an uninterrupted bluetooth connection. If you are using your board in a scenario where the bluetooth connection is unstable/interrmitent, then logging to the board’s built-in memory may be a useful alternative. It is important to note, however, that the onboard memory is limited. More on this as we progress through this post.
We will need to import some of the MetaWear-related logging tools (not to be confused with the Android Log utility):
import com.mbientlab.metawear.module.Logging;
import com.mbientlab.metawear.data.CartesianShort;we create another couple of variables with our other variable declarations:
private static final String LOG_KEY = "accel_log";
//...other variables
private Logging loggingModule;and finally use the getModule method once we’re connected to the board:
@Override
public void connected() {
Log.i(TAG, "Connected");
try {
ledModule = mwBoard.getModule(Led.class);
accelModule = mwBoard.getModule(Accelerometer.class);
loggingModule = mwBoard.getModule(Logging.class); //add this line
} catch (UnsupportedModuleException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}Now we will update our switch listener, which we previously used for streaming, so that it logs the data instead. Within the onCheckChanged function we update the following:
public void onCheckedChanged(CompoundButton buttonView, boolean isChecked) {
Log.i("Switch State=", "" + isChecked);
if (isChecked) {
accelModule.setOutputDataRate(ACC_FREQ);
accelModule.setAxisSamplingRange(ACC_RANGE);
accelModule.routeData()
.fromAxes().log(LOG_KEY)
.commit().onComplete(new CompletionHandler<RouteManager>() {
@Override
public void success(RouteManager result) {
/*
result.subscribe(STREAM_KEY, new RouteManager.MessageHandler() {
@Override
public void process(Message message) {
CartesianFloat axes = message.getData(CartesianFloat.class);
Log.i(TAG, axes.toString());
}
});
*/
result.setLogMessageHandler(LOG_KEY, new RouteManager.MessageHandler() {
@Override
public void process(Message msg) {
final CartesianShort axisData = msg.getData(CartesianShort.class);
Log.i(TAG, String.format("Log: %s", axisData.toString()));
}
});
}
@Override
public void failure(Throwable error) {
Log.e(TAG, "Error committing route", error);
}
});
loggingModule.startLogging();
accelModule.enableAxisSampling();
accelModule.start();
} else {
loggingModule.stopLogging();
accelModule.disableAxisSampling();
accelModule.stop();
}Note the 4 key changes:
- Change the
streammethod tolog - Change the STREAM_KEY to LOG_KEY
- Remove (in the above example it is commented out)
result.subscribeand replace withresult.setLogMessageHandler - Add the
startLoggingandstopLoggingmethods - note that they should be called before enabling/disabling axis sampling
Now the log is being recorded when we toggle the switch on. However, in order to actually access these logs, we need to add the downloadLog method. For simplicity, we include this in the toggle switch off else statement, though you could trigger it in many other ways, such as with a separate onClick listener on a new button:
} else {
loggingModule.stopLogging();
accelModule.disableAxisSampling();
accelModule.stop();
loggingModule.downloadLog(0.05f, new Logging.DownloadHandler() {
@Override
public void onProgressUpdate(int nEntriesLeft, int totalEntries) {
Log.i(TAG, String.format("Progress= %d / %d", nEntriesLeft,
totalEntries));
}
});
}The first argument in the downloadLog method specifies how often to send progress updates, expressed as a fraction between [0, 1] where 0= no updates, 0.1= 10 updates, 0.25= 4 updates, etc.
Finally, let’s check our board’s memory after downloading the log:
loggingModule.downloadLog(0.05f, new Logging.DownloadHandler() {
@Override
public void onProgressUpdate(int nEntriesLeft, int totalEntries) {
Log.i(TAG, String.format("Progress= %d / %d", nEntriesLeft,
totalEntries));
}
});
Log.i(TAG, "Log size: " + loggingModule.getLogCapacity());Now when you toggle the switch off, you should see the logs in the logcat, as well as regular download progress updates:
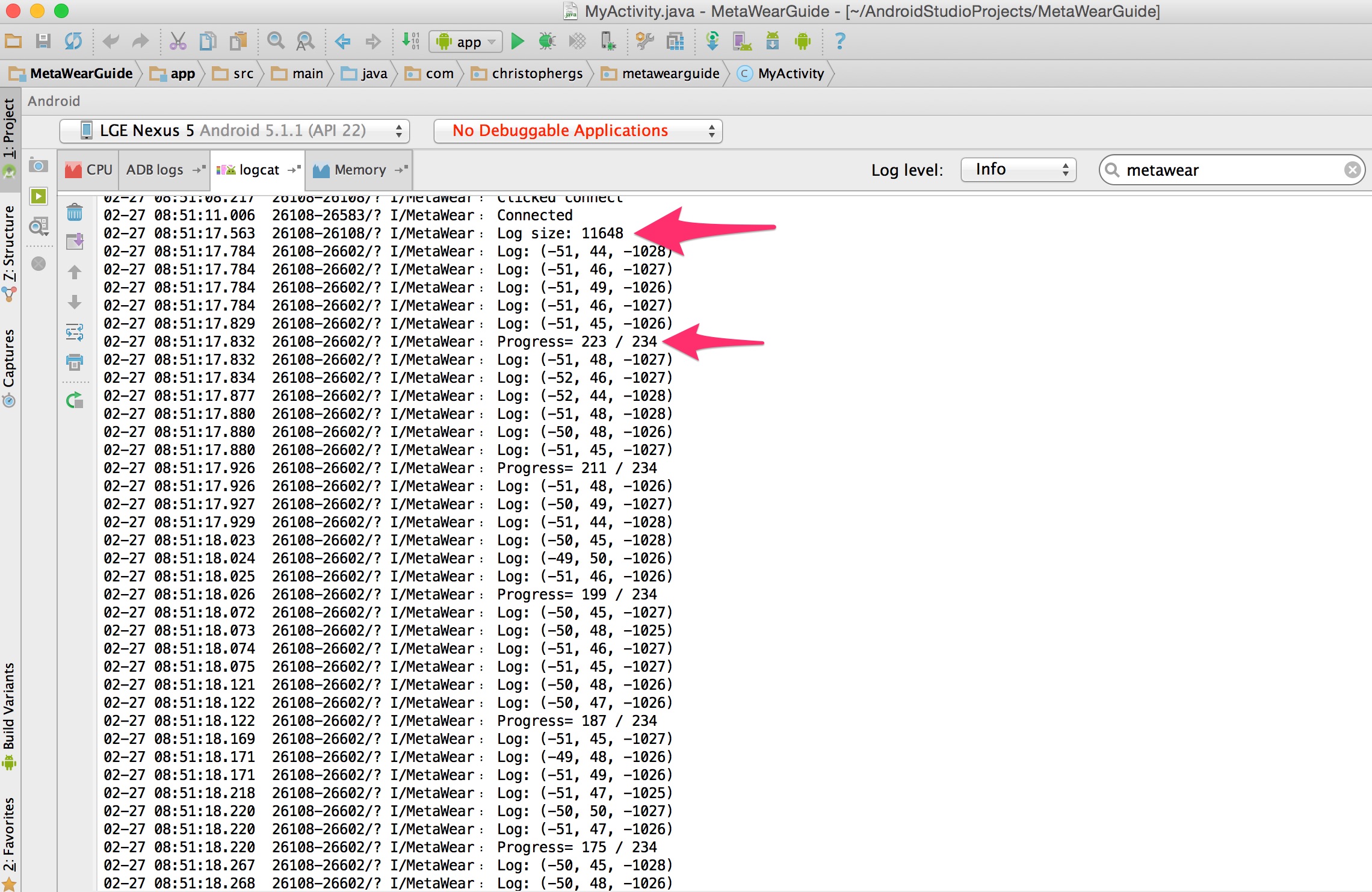
Our logging is now setup. It’s important to note that you cannot stream and log on the same route. Also, simultaneously streaming and logging data is not a recommended use case.
A few additional details on this topic:
If we wanted to clear the board memory we can use clearEntries() but the erase operation will not be performed until you disconnect from the board.
If you wanted to overwrite previously logged data, you call startLogging(True), where the boolean argument should be set to True to overwrite older entries if the onboard log is full.
There are lots of other nuances to logging, check the detailed documentation for more information.
Now you should understand the key concepts of interacting with the board. In the next post we will consider how to stream data from the accelerometer and the gyroscope at the same time.
Note You can view all these changes in the github repository on the branch version-0.5